A diode is a two pin passive device. Shape wise these diodes look similar to a 1/2 or 1/4 watts resistor. Briefly, diode is a one way street for electric current. Diodes will let current pass in one direction, but will block the current in the other directions. Very much similar to a valve put in the bi-cycle tires, which lets air to come in from one direction but doesn't let the air go out in opposite direction. Technically you can say that diode provides high resistance to current in one direction and low resistance in opposite direction

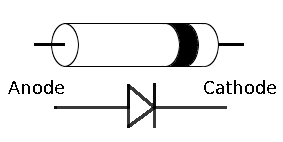
The above figure shows diode characteristics in forward and reversed direction. General symbol of diode is represented as shown below.
Diode forward Biasing : When current enters from anode diode allows all the current to pass through them. Here the diode is said to be in forward biased (since it is forwarding all current). Remember that in forward bias diode drops around 0.7V and this value varies with the temperature.
Diode reversed Biasing : When current enter from cathode it will get blocked by diode and won't appear at anode. Here the diode is said to be in reversed bias. Ideally a diode should block all the current in reversed biased but practically they let very small amount of current to pass through, which is called leak current. Since this current is very small for some circuits you may ignore it.
Please note that direction of current makes diode forward or reversed biased and behave accordingly.
General purpose diodes are rated by two main properties, these are break down voltage and max current. These two ratings should be considered before using diode in any circuit
Break down voltage : This is the maximum voltage at which a diode can withstand reverse biased mode. It means upto this voltage diode shall put in all its effort to stop current to flow, since it is put in reversed bias. But if the voltage goes above this the diode will break down and all the current will pass through it. During design itself, proper care should be taken about selection of diode based on "break down voltage".
I.e. suppose your circuit works on 50V ac and you have used diode as a rectifier then "Break down voltage" of diode should be greater than 50V.
Max current rating : This is the maximum current the diode can tolerate in forward bias. General purpose diodes pass current only when they are in forward bias. Every electronic component generates heat when current passes through it, same is the case of diode also. If you try to pass current more than "max current rating" the heat generated will be so much that it will blow up the diode itself. To answer this problem high current rating diodes come with metal cap on them. The metal cap is called heat sink and helps in reducing diode's temperature.
